Enhancer/Promoter Library Construction
VectorBuilder can help you construct high-complexity enhancer/promoter libraries to functionally assess cis-regulatory elements in modulating gene expression. Typically, constructing an enhancer/promoter library involves placing the cis-regulatory elements upstream or downstream of a reporter gene, with the reporter gene transcripts as the readout of enhancer/promoter activity measured by NGS.
Highlights
- Diverse cloning strategies: Tailored to your research goals, we employ various approaches to construct your enhancer/promoter library.
- High complexity: We can generate enhancer/promoter libraries exceeding 108 in complexity.
- Optimized vector design: Our vector design exhibits a high signal-to-noise ratio, addressing a common bottleneck in enhancer/promoter screening.
- Fluorescent reporter: Integration of a fluorescent reporter facilitates both visualization and cell sorting.
- Barcodes: Incorporating barcodes enables the identification of the transcriptional activity of upstream regulatory elements through NGS analysis.
Service Details
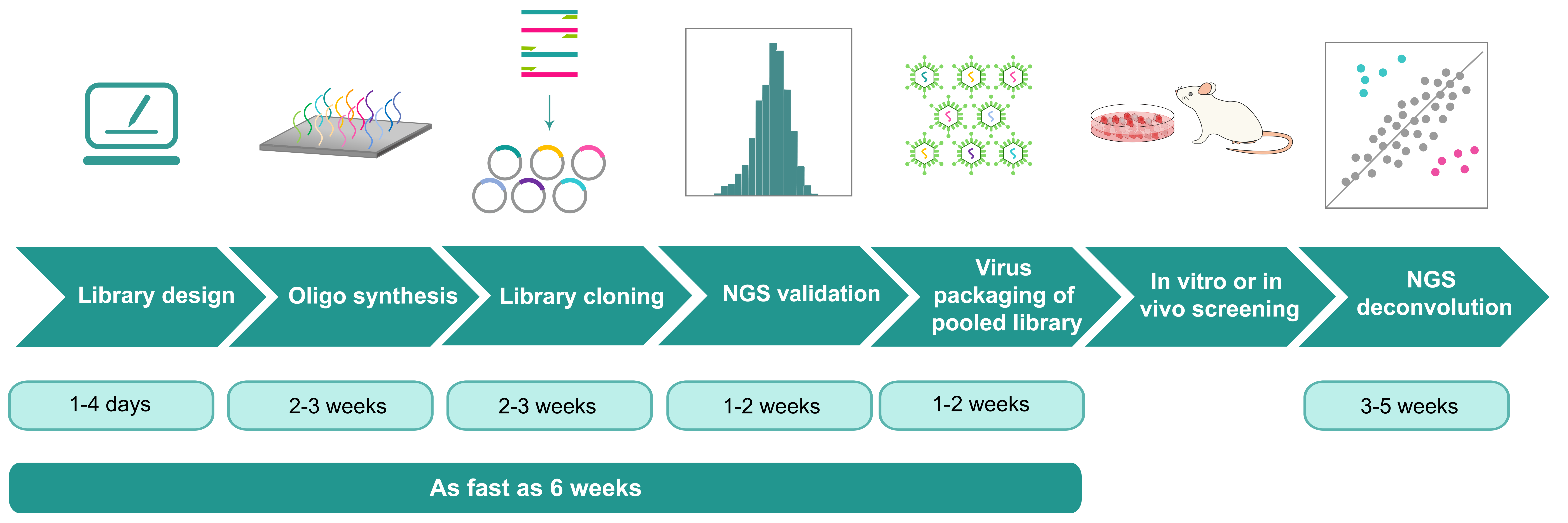
Price and turnaround Price Match
| Service Module | Brief Description | Price (USD) | Turnaround |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancer/promoter library design | VectorBuilder's team of highly experienced scientists will design custom enhancer/promoter libraries for you, featuring a high signal-to-noise ratio, your selected fluorescence markers, and variable barcodes in our validated backbones. | Free | 1-4 days |
| Pooled library cloning | Includes oligo/gene synthesis, massive parallel cloning of inserts for variable regions into desired vector backbone, preliminary validation by Sanger sequencing, and full validation by NGS. Deliverable includes library in E. coli glycerol stock and NGS report. | From $2,300 | 5-8 weeks |
| Virus packaging of pooled library | Please click here to view detailed info of virus packaging services. The price for packaging pooled library is 1.5-fold of the price for packaging single vector. | ||
| NGS deconvolution of post-screening sample | Includes NGS library preparation from total RNA or mRNA of screened cells, Illumina sequencing (>500x coverage), and data analysis. | From $320 per sample | 3-5 weeks |
Technical Information
Enhancer/promoter library construction strategies
Chip-based oligo synthesis
Chip-based oligo synthesis is ideal for generating pre-designed enhancer/promoter variants with various sizes and sequences. Our chip-based DNA synthesis can usually go up to 300 nt with a low error rate.
Obtained from genomic DNA
Variable fragments of an enhancer/mutation library can be obtained from genomic DNA or bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) through probe hybridization. Pre-designed probes are employed to capture and enrich putative regulatory elements from the genomic sequence or BAC. Additionally, an unbiased shotgun-type approach can be utilized to obtain potential regulatory elements from the genomic DNA. Subsequently, these fragments will be cloned into vector backbones and subjected to screening for further characterization.
Directed evolution from existing regulatory elements
The construction of enhancer/promoter libraries can be based on existing sequences of these regulatory elements. By employing various mutagenesis strategies, such as error-prone PCR, utilization of degenerate codons, or DNA shuffling, novel variants are generated. These variants can subsequently undergo screening processes to identify those with desired traits, facilitating the targeted evolution of regulatory elements.
Key components
Vector design for enhancer library

Figure 1. Key vector components for an enhancer library.
Enhancer: The enhancer sequence to be screened can be inserted either upstream or downstream of the reporter gene. When the enhancer is positioned downstream (A) of the reporter gene and before the poly(A) signal, it is transcribed alongside the reporter gene and, therefore, can be measured directly by mRNA-seq. When positioned upstream (B) of the reporter gene, a barcode sequence is commonly incorporated in the 3’ UTR region of the reporter gene and can be transcribed with the reporter gene. The barcode serves as the proxy of the enhancer and can be sequenced by mRNA-seq.
Minimal promoter: A user-selected minimal promoter sequence is placed here. This will drive transcription of the downstream reporter if an enhancer element is present to activate the transcription. In the absence of such enhancer, the minimal promoter will be almost completely inactive.
Click to view more information about commonly used minimal promoters
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
Reporter: A visually detectable bright fluorescent protein gene (such as GFP) or a chemiluminescent protein gene (such as luciferase). This allows highly sensitive detection of enhancer activity.
Barcode: Enhancer library barcodes are unique, short sequences within individual plasmids. After screening, the read count of each barcode is determined through NGS analysis. By correlating the unique barcode sequences with the specific enhancer variants, the transcriptional activity of particular enhancers can be identified.
SV40 late pA: Simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination of the upstream ORF.
Vector design for promoter library
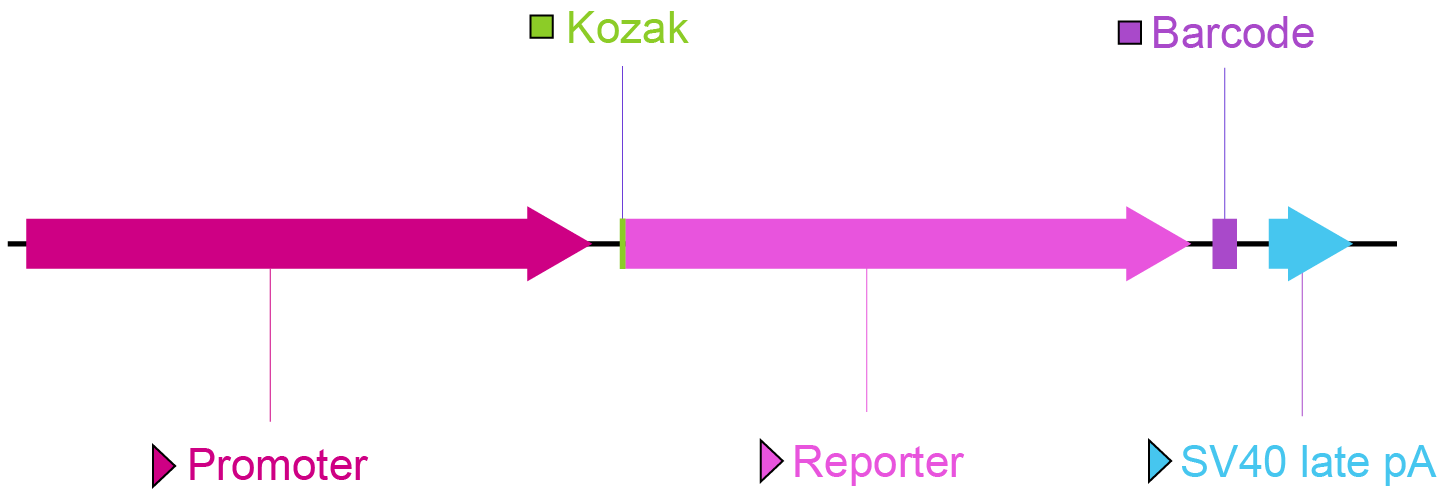
Figure 2. Key vector components for a promoter library.
Promoter: The promoter sequence to be screened can be inserted here to drive the transcription of the reporter.
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
Reporter: A visually detectable bright fluorescent protein gene (such as GFP) or a chemiluminescent protein gene (such as luciferase). This allows highly sensitive detection of promoter activity.
Barcode: Promoter library barcodes are unique, short sequences within individual plasmids. After screening, the read count of each barcode is determined through NGS analysis. By correlating the unique barcode sequences with the specific promoter variants, the transcriptional activity of particular promoters can be identified.
SV40 late pA: Simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination of the upstream ORF.
Experimental data
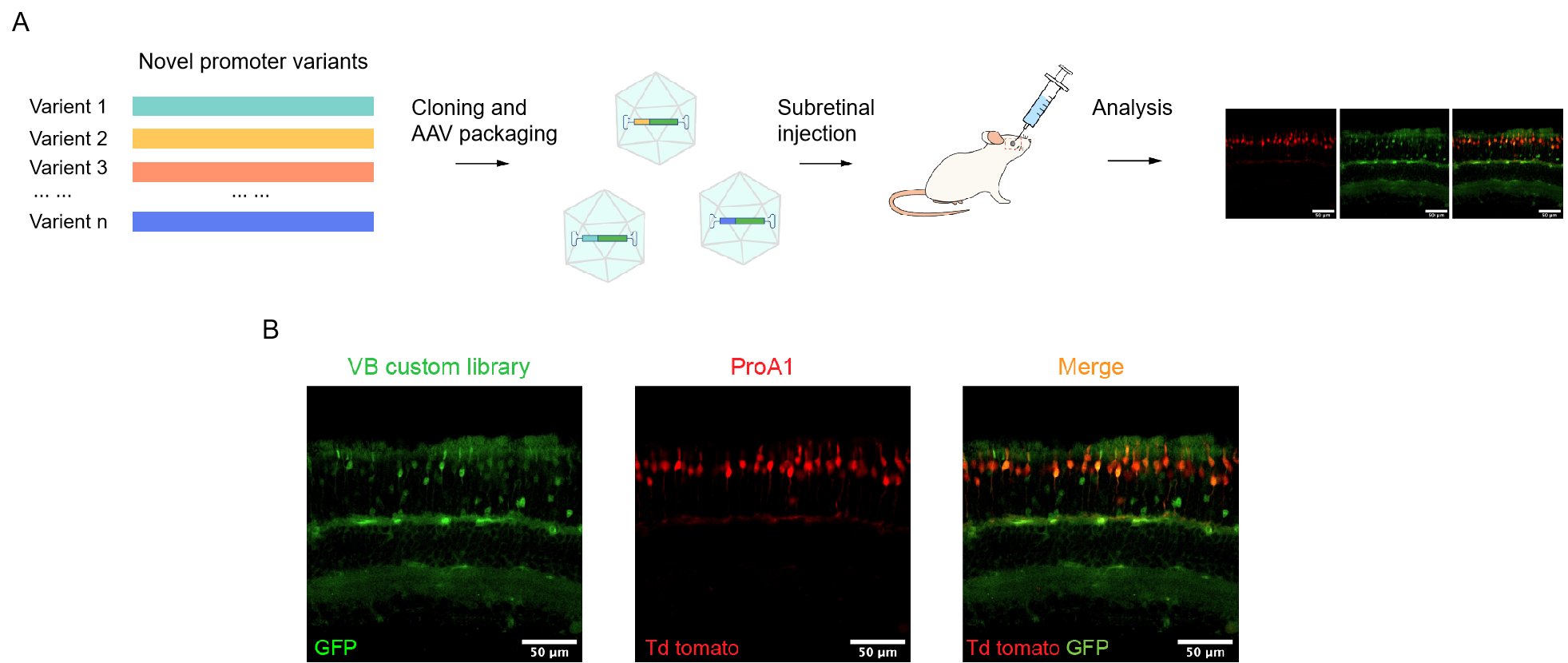
Figure 3. A cone-specific promoter library construction and screening. (A) Experimental workflow. Novel promoter variants were generated and cloned into the AAV backbone, driving the expression of a GFP reporter. The AAV promoter library was injected into the subretinal region of mice and subsequent screening and analysis were performed. (B) Subretinal expression pattern of the library. The AAV promoter library driving GFP was co-injected with another AAV carrying ProA1 promoter driving Td Tomato. ProA1 is a known cone-cell-specific promoter. Co-localization of the red and green fluorescence indicated the presence of cone-specific promoters in the promoter library.
How to Order
Customer-supplied library plasmid pool
If the customer-supplied premade plasmid pools are used, please send us the materials following the Materials Submission Guidelines. Please strictly follow our guidelines to set up shipment to avoid any delay or damage of materials. All customer-supplied materials undergo mandatory QC by VectorBuilder which may incur a $100 surcharge for each item. Please note that production may not be initiated until customer-supplied materials pass QC. For customer-supplied premade plasmid pools, we cannot provide any guarantees regarding the complexity or uniformity of the library.



